As a very important part of the power system, the energy meter is mainly to measure the electrical energy consumed in the circuit. With the development of the times and the progress of the social economy, the development of electric energy meters has now undergone a long process.
The appearance and development of electric energy meters in the world has a history of more than 100 years. The earliest electric energy meters were made according to the principle of electrolysis in 1881. Although these electric meters each weighed several tens of kilograms, they were very cumbersome and without The guarantee of precision, however, was still regarded as a major invention in the scientific and technological circles, and it was quickly praised and praised in engineering. With the development of science and technology, the discovery and application of AC in 1888 Inductive energy meters were born.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the long-life electric energy meter, mechatronics electric energy meter (semi-electronic electric energy meter), all-electronic electric energy meter, multi-function all-electronic electric energy meter, prepaid electric energy meter, multi-rate electric energy meter The maximum demand meter, loss meter, etc. are used.
In the 1990s, some electronic energy meters were introduced, which pushed the development of electric energy meters further. The advantages of the electronic energy meter are small size, light weight, high sensitivity, high precision, easy calibration and installation, and strong overload capability, and pulse signal output, which provides favorable conditions for automatic meter reading.
Beginning in 2000, it began to vigorously develop smart energy meters, which are a new type of all-electronic energy meter with functions of energy metering, information storage and processing, real-time monitoring, automatic control, information interaction, etc., supporting two-way metering, ladder price, The actual needs of time-sharing electricity prices, peak-to-valley electricity prices, etc., are also the technical basis for implementing distributed power metering, two-way interactive services, smart homes, and intelligent communities. It can also automatically alarm the residents' electricity load to avoid serious accidents such as short circuit and fire caused by overload. In addition, residents can use the recharge card or online recharge to pay the electricity fee, which is convenient and quick.
Inductive meter works
Inductive single-phase electric energy meter, also known as mechanical single-phase electric energy meter, is designed by the principle of electromagnetic induction. When the meter is connected to the circuit under test, the voltage U of the circuit under test is applied to the voltage coil, and an alternating magnetic flux is formed in the core. A part of the flux ΦU is passed from the return pole to the aluminum disk. In the iron core of the voltage coil; similarly, after the current I of the circuit under test passes through the current coil, an alternating magnetic flux Φi is also formed in the U-shaped iron core of the current coil, and the magnetic flux is formed by U to form one end of the iron core. It goes through the aluminum pan from bottom to top and then from top to bottom through the aluminum pan to the other end of the U-shaped iron core. The circuit and magnetic circuit of the watt-hour meter are shown in Figure 6-3. The re-magnetic plate 4 is made of steel plate, and its lower end extends into the lower part of the aluminum plate, and the core of the aluminum plate and the voltage component. The columns correspond to form a loop for the working current of the voltage coil.
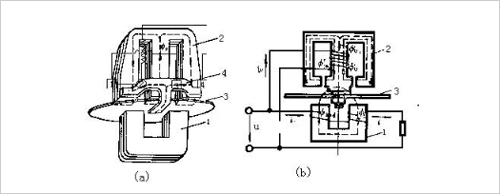
(a) core structure (b) circuit and magnetic circuit
Since the two magnetic fluxes passing through the aluminum disk are AC magnetic fluxes and are passed through the aluminum disk at different positions, induced eddy currents are generated in the vicinity of the magnetic flux and the eddy current flowing through the aluminum disk. As shown in the figure, the interaction of the two magnetic fluxes with these eddy currents produces a rotational moment on the aluminum disk that drives the rotation of the aluminum disk.
The rotational moment MP acting on the aluminum disk is proportional to the active power of the circuit under test. When the aluminum disk starts to rotate under the action of the rotational moment, the magnetic flux Φf of the yong permanent magnet that cuts through it will generate a eddy current if. The interaction of this eddy current with the yong permanent magnet will produce a moment Mf acting on the opposite direction of the rotation of the aluminum disk, called the braking torque. Obviously, the faster the aluminum disk rotates, the faster the magnetic field line that cuts through it, and the greater the rate of change of magnetic flux caused. The larger the eddy current is, the larger the braking torque is. When the aluminum disk is not moving, The braking torque does not exist. The braking torque is generated by the rotation of the aluminum disk and increases with the increase of the rotational speed. The direction is always opposite to that of the aluminum disk.
When the aluminum disk starts to rotate under the action of the rotating torque, as the rotational speed increases, the braking torque increases continuously until the braking torque is balanced with the rotational torque. At this time, the total torque acting on the aluminum pan is zero, and the rotational speed of the aluminum pan is no longer increased, but is stabilized at a certain rotational speed.
Smart meter
The intelligent electric energy meter is composed of a measuring unit, a data processing unit, a communication unit, and the like, and has an electric energy meter such as electric energy metering, data processing, real-time monitoring, automatic control, and information interaction. The smart meter recharges the smart IC card and inputs it into the meter through the user's payment. The meter can supply power, and the meter automatically cuts off the power after the battery is used up, thus effectively solving the problem of difficulty in meter reading and power collection. It also implements computer management for the user's electricity purchase information, which is convenient for inquiries, statistics, charges and printing of tickets.
Compared with ordinary mechanical electric energy meters, smart meters have the advantages of more accurate measurement, intelligent deduction, electricity price inquiry, power memory, balance alarm, and information remote transmission.
Classification of smart meters
At present, domestic smart energy meters are mainly divided into two types: one is electromechanical and the other is all electronic.
Electromechanical integration
The electromechanical integration means that a certain component is attached to the original mechanical watt-hour meter, so that it can not only accomplish the required functions, but also reduce the cost and is easy to install. Generally, the design scheme is not to destroy the original meter. The physical structure, without changing its national measurement standards, adds a sensor device to a smart meter that also has an electrical pulse output while mechanically counting.
The first type of electromechanical combined watt-hour meter is based on the original mechanical watch, with electronic counting device and corresponding control and communication circuit, or IC card reading and writing interface to realize automatic metering and control. The basic structure is to punch or coat (paste) the material on the turntable of the original mechanical watt-hour meter, and transform the rotation of the mechanical turntable into an electrical pulse signal through photoelectric conversion, and then perform corresponding counting processing. Because of the fact that the metering principle has not been changed, the metering accuracy and characteristics are exactly the same as those of the mechanical meter, and the cost is relatively high.
Another type of electromechanical-coupled watt-hour meter uses an electronic metering circuit to obtain a power count value after driving a digital pulse signal through a micro-motor. This structure is the most compact and feasible electronic watt-hour meter. The solution, but unfortunately the higher requirements on the metering circuit, that is, all the tables are required to convert the energy value into a corresponding number of digital pulses at a fixed ratio, in order to drive the micromotor at the correct speed to rotate the character wheel. . This ratio is the so-called meter constant (imp/kWh). Since the timing components used in the circuit to determine the pulse speed are mostly RC components with large discrete parameters, in order to ensure the metering accuracy and product consistency of the meter, It is necessary to strengthen the screening of components and the adjustment of semi-finished products in the production process, that is to say, it is necessary to increase the corresponding manpower and material resources and to extend the production cycle, thereby increasing the production cost and cost of the electricity meter. . In addition, the watt-hour meter of this structure is no different from the old-fashioned mechanical watch in data collection and user payment methods, and should be eliminated.
All-electronic smart meter
All-electronic smart meters use electronic devices with integrated circuits as the core from metering to data processing, thus eliminating mechanical components. The all-electronic smart meter is smaller than the mechatronic smart meter, with higher reliability, more accurate, less power consumption, and greatly improved production process. The all-electronic smart meter will gradually replace the meter with mechanical parts, which is the general trend of future social development.
The all-electronic watt-hour meter system consists of:
1, far pass table. The meter with pulse output, such as water meter, electric meter, gas meter and heat meter, is a remote meter. The metering method is the same as that of the traditional meter. The difference is that the pulse output function is added to the original base meter. Each pulse represents a certain metering value. . The collector collects pulses through the remote meter pulse output port.
2, the collector. The collector can simultaneously collect the pulse information of the water meter, the electric meter, the gas meter, the heat meter and the like, and convert the pulse information into the physical quantity of the metering and approval, and store it in the memory of each collector, and can query the arbitrary system in the system by controlling the microcomputer. The energy consumption information of a household, and the user information is uploaded under the command of the meter reading of the microcomputer.
3, the converter. The main task of the converter is to complete the data communication with the collector, issue the power data freeze command to the collector, receive the power data of the collector periodically or receive the data of a certain meter or a group of meters according to the system requirements. According to the system requirements, the communication with the primary station is completed, and the information required by the primary station such as the user's power data is transmitted to the primary station database. The downlink channel refers to the communication line between the converter and the collector, mainly including the bus meter reading system, the carrier meter reading system and the infrared meter reading system. The communication channel uplink channel refers to the communication line between the converter and the main station, and can be used for communication media such as dian, wireless, and dedicated lines.
4. System management software functions. The system management software is based on communication, with database as the core, providing functions such as data processing, query, statistics, report, backup, etc. It adopts a combination of object-oriented and modular methods to flexibly support different customer requirements, such as special format reports. Permission control, etc.; with the customer's original governance system, can interface with other management software, provide data interface and communication interface, with network communication function; can manage multiple cells at the same time, set communication parameters for each cell; meter management, set meter Original parameters, address, and status; rate management, can set a variety of rates, set the unit price of each energy; user governance, governance and control of each household's usage, governance user settlement methods; real-time meter reading function, The system can copy the real-time data of each energy meter; the automatic calculation of the cost can realize the even distribution of the public energy loss or share it proportionally to each household and automatically calculate the payability of each production according to the table data and unit price, so as to Charge; print function, print the list of user usage; query function, you can query the consumption of any household, all households in any unit and all households in the whole community at any time. Information.
How smart meters work
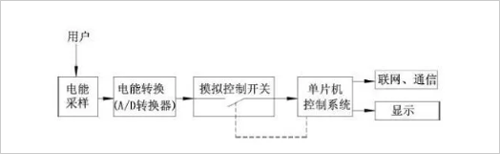
The following figure is a block diagram of a smart meter:
The figure below is a hardware design diagram:
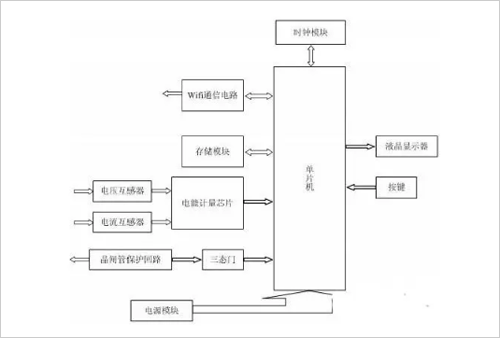
The smart meter is mainly composed of electronic components. Its working principle is to use the special energy meter integrated circuit to process the sampled voltage and current signals and convert them into pulses proportional to the electric energy by real-time sampling of the user's power supply voltage and current. The output is finally processed and controlled by the single-chip microcomputer, and the pulse is displayed as the power consumption and output. Usually, the number of pulses emitted by the A/D converter when the smart meter is measured once is called the pulse constant. For the smart meter, this is an important constant because the A/D converter is in unit time. The number of pulses sent will directly determine the accuracy of the meter.
At present, most smart meters use the design principle of one A/D converter. However, some manufacturers produce multi-user centralized smart meters that use multiple A/D converters, so that the measurement of electric energy can only be used. When queued up, it will cause a decrease in measurement accuracy.
Smart meter sampling method
The current electronic energy meter has two main forms of user power sampling, one is to use the transformer to sample, and the other is direct sampling.
Using the transformer to sample is to use the voltage transformer and current transformer to separately collect the user's voltage signal and current signal; and the direct sampling is to use a high thermal stability resistor divider network to obtain the voltage signal, using the manganese oxide with a small temperature coefficient of resistance The chip performs direct current sampling.
With transformer sampling, it is not as good as direct sampling in terms of starting current, linear range, power consumption and accuracy, especially when the current value is small. The advantages of transformer sampling are strong anti-interference, simple circuit and low cost. For example, when the rated current is 20A, the direct sampling current is 20mA, and the starting current of the transformer sampling is 40mA. For example, the error of the full electronic energy meter using the dedicated manganese copper sheet for direct current sampling can be adjusted to +0.5%, and the current transformer is used for sampling. If no compensation measures are taken, the error of the transformer itself may exceed 5%.
Smart meter reading scheme
As a basis for the measurement of electricity charges, the meter is related to meter reading. From the current technology, there are mainly IC card type and remote meter reading.
The IC card meter charging system has low cost, high reliability and long service life. The IC card uses silicon (EEPROM) to store information. An IC card can be used for at least 10 years. The IC card meter charging system is highly secure, not easy to copy, and the charges are correct and not easy to make mistakes. It has strong encryption. The use of the IC card meter charging system can improve the governance level of residential electricity charges, and ensure that the electricity part can receive the electricity fee in time (the user will not be able to continue to buy electricity, will be powered off). The system functions of the IC card table include pre-charge function, alarm function, power-off function, display function and encryption function.
The entire charging system of the IC card table includes a host computer, an IC card meter and an IC card. The IC card meter charging system realizes the electronic charging of electricity, and the technology is mature and reliable. Therefore, the IC card charging system has been widely promoted in China. However, from a system perspective, since the user terminal and the system host are not directly lian, the user can only know the user's situation when the card is paid by the user, and the information feedback is lagging. It can be said that the user terminal is still out of line with the entire network. From the economic point of view, the power supply is charged first and the electricity is not in line with economic policies. It can be said that the interests of users are infringed on certain procedures. Therefore, many cities have in principle no longer approved new IC card table items in the long run. Look, the IC card charging system can only be used as a transitional product.
The remote automatic meter reading system realizes automatic copying of power consumption data, and can eliminate all the drawbacks of manual operation. The user's electricity consumption data can be directly entered into the computer management system of the electricity business. The electricity management staff can monitor the power usage situation at any time, and find problems (such as faults, electricity theft, etc.) in time. The line loss directly affects the economic benefit of the power supply part. In the past, the line loss situation could not be correctly measured regardless of the manual reading or the IC card table. It is also difficult to find the cause of the line loss, and the meter reading can be obtained almost simultaneously after the remote meter reading. And the total reading of the sub-table, to grasp the line loss situation at any time, and easier to analyze the cause of the line loss for processing. With the development of the situation, residents open personal accounts in banks, business computer governance systems and banks to network, complete the automatic copying, processing, bank transfer fees and other full operations, can truly achieve automation of power management. At present, the domestic remote meter reading system mainly has two forms: 485 bus and carrier meter reading. The carrier set copying system uses a dedicated chip to modulate and demodulate the power consumption data, and communicates through the power line to realize centralized meter reading. The 485 bus mode has high reliability of data transmission and low cost. The disadvantage is that it requires wiring, and the installation is complicated. In addition, the cable is easily damaged by humans. In particular, many communities do not agree to pull lines, making this bus method difficult to construct. Nowadays, more schemes are adopted: the user terminal uses the power line carrier communication to the data concentrator, and the data concentrator uses the dedicated dian telephone line to the upper computer. Of course, depending on the different conditions of the cell, there are also many solutions that use the 485 bus in conjunction with the power carrier.
Since the power consumption data of the all-electronic smart meter has been digitized, it can be conveniently combined with various data collection and transmission circuits to form an automatic metering and billing system, which is a replacement product of the current household electric meter, and a large amount of such products are used. It will save a lot of meter reading calculation work in the power supply department, and can recover electricity charges in time, that is, pay for electricity first, which has huge economic and social benefits. Such smart meters have two common meter reading schemes: centralized bus metering and power carrier centralized meter reading. Both are remote meter reading.
Centralized meter reading by the bus system: the electric meter part adopts the smart meter, the smart meter signal lines of each household are connected to one bus, the bus is connected to the downstairs adapter, and the interconnects of each building are connected with the concentrator of the cell, and the concentrator is connected. Centralized power supply.
Power carrier meter reading: A centralized meter reading system that directly uses existing low-voltage transmission lines for data transmission, eliminating the need for laying lines, and has obvious advantages.
The system is a high-tech product integrating microelectronics technology, communication technology and computer technology. It has the characteristics of high reliability and simple installation. It is widely used in urban and rural electricity meter, gas meter copying, billing and monitoring. However, since the power line transmits power to the powered equipment instead of transmitting data, the power line has many restrictions on data transmission: (1) the distribution transformer has a blocking effect on the power carrier signal, so the power carrier signal can only be (1) Different signal coupling modes have different signal losses to the power carrier; (3) Power lines inherently have inherent pulse interference. In addition, the high power cut, high noise and high distortion make the power line an unsatisfactory communication medium. However, due to the development of modern communication technology, power line carrier communication is possible. The signal-to-noise ratio of the data signal determines the distance of the transmission distance. . The key to power line carrier communication is to select a powerful Modem chip for power line carrier.
The working characteristics of smart meters
Smart meters not only use the design of electronic integrated circuits, but also have remote communication functions, which can be networked with computers and controlled by software. Therefore, compared with inductive meters, smart meters have very good performance and operational functions. Big advantage.
1. Power consumption: Since the smart meter adopts the electronic component design method, the power consumption of each meter is generally only about 0·6w~0·7w. For a multi-user centralized smart meter, the average power to each household is smaller. Generally, the power consumption of each inductive meter is about 1. 7W.
2. Accuracy: In terms of the error range of the meter, the error of the 2. 0-class electronic energy meter measured within the range of 5% to 400% of the calibration current is ±2%, and the accuracy level currently used is 1·. Level 0, the error is smaller. The inductive meter has an error range of +0·86%~-5.7%, and the inductive meter is getting slower and slower due to mechanical wear and tear, and the final error is getting larger and larger. State Grid has conducted spot checks on inductive meters, and found that after more than 50% of inductive meters have been used for 5 years, the error has exceeded the allowable range.
3, overload, power frequency range: the overload meter of the smart meter can generally reach 6 to 8 times, with a wide range. At present, the 8~10 rate table is becoming more and more users' choices, and some can even reach a wide range of 20 times. The working frequency is also wide, ranging from 40HZ to 1000HZ. Inductive meters generally have an overload factor of only 4 times, and the operating frequency range is only between 45 and 55 Hz.
4. Function: Since the smart meter adopts the electronic watch technology, it can be networked with the computer through the relevant communication protocol, and the hardware control and management can be realized through the programming software. Therefore, the smart meter not only has the characteristics of small size, but also has the functions of remote control, multi-rate, identification of malicious load, anti-stealing, prepaid power, etc., and can be modified by modifying different parameters in the control software. Different requirements for control functions that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional inductive meters.
Qing Dao
The Qing Dao, also known as the Qing Dynasty sword or the Qing Dao Dao, is a traditional Chinese sword that originated during the Qing Dynasty (1644-1912). It is a single-edged, curved blade with a length typically ranging from 70 to 100 centimeters.
The hilt of the Qing Dao is usually made from materials like wood, bone, or horn, and is ergonomically designed to provide a comfortable grip. The sword's guard, known as the tsuba, is often intricately decorated with various motifs, such as dragons, flowers, or other traditional Chinese symbols.
The Qing Dao was primarily used by the military and martial artists during the Qing Dynasty. It was a favored weapon among cavalry units due to its versatility and effectiveness in close combat. The sword's curved blade allowed for swift and powerful strikes, making it a formidable weapon on the battlefield.
In addition to its military applications, the Qing Dao is also highly regarded as a symbol of status and prestige. It is often seen as a cultural artifact, representing the rich history and heritage of China. Today, the Qing Dao sword is still produced and used in traditional Chinese martial arts, as well as being sought after by collectors and enthusiasts worldwide.
Qing Dao Sword, Chinese Qing Dao, Qing Broadsword
Ningbo Autrends International Trade Company , https://www.longquan-swords.com


